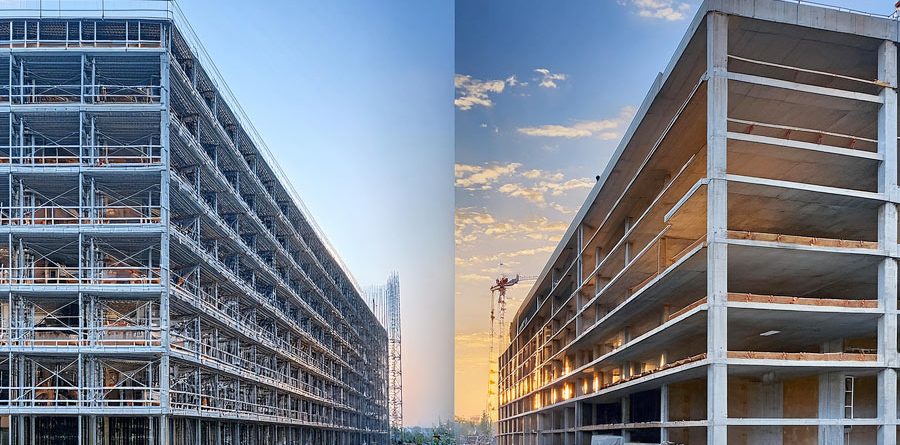
Light Steel Structures vs Reinforced Concrete Structures: The construction industry thrives on innovation, efficiency, and adaptability, making material selection pivotal to the success of any project. Among the most widely utilized building materials today are light steel structures and reinforced concrete structures. These materials are the backbone of modern construction, with each offering unique strengths tailored to different project requirements. The decision between the two significantly impacts key factors such as construction timelines, cost-efficiency, durability, environmental sustainability, and design adaptability.
In recent years, light steel structures have garnered increasing popularity due to their distinct advantages, revolutionizing how we approach residential, commercial, and industrial construction projects. This comprehensive analysis compares the two approaches to help stakeholders make informed decisions.
A Comparative Analysis of Light Steel Structures vs. Reinforced Concrete Structures
1. Assembly and Construction Time: Fast and Efficient Solutions
Speed is a defining characteristic of light steel structures. Unlike traditional construction methods, these structures benefit from the prefabrication process, where steel profiles are meticulously manufactured in factory-controlled environments. This precision ensures that components arrive on-site ready to assemble, drastically reducing construction time.
For instance, producing light steel profiles for a two-story building can take as little as 10 hours in a factory setting. Once delivered, these profiles can be erected on-site in approximately two days, following detailed assembly plans. This efficiency is invaluable for projects operating under tight deadlines, such as disaster relief housing, commercial spaces, or modular expansions for schools and hospitals.
Conversely, reinforced concrete structures demand significantly more time due to the sequential nature of their construction processes. Formwork preparation, steel reinforcement placement, concrete pouring, and curing are labor-intensive tasks that may extend over several weeks. Moreover, these steps are vulnerable to external factors such as weather conditions, which can delay progress further. For instance, rain can halt concrete pouring, while freezing temperatures might compromise curing processes, leading to extended timelines.
The faster assembly of light steel structures makes them particularly advantageous for projects where time is of the essence, including temporary shelters or rapidly growing urban areas where delays can lead to financial penalties or resource constraints.
2. Material and Cost: Economical and Portable Solutions
Cost-effectiveness is another significant advantage of light steel structures. Their lighter materials reduce transportation expenses and streamline on-site labor requirements. Since the profiles are manufactured with high precision in factories, material wastage is minimized, cutting down on unnecessary expenses.
For example, in projects utilizing light steel, the material’s portability and the lack of heavy machinery requirements can reduce overall logistical costs by up to 20-30%, particularly in remote areas. This economy is especially beneficial for smaller-scale developments like tiny houses or modular office buildings.
On the other hand, reinforced concrete structures often incur higher costs due to the extensive resources involved. The quality of concrete, the placement of steel reinforcements, and the skilled labor required for these processes can drive up expenses. Additionally, the transportation of bulky materials such as cement, sand, gravel, and steel bars adds logistical challenges, especially in areas with limited infrastructure.
In larger projects, such as multi-story buildings, reinforced concrete structures might provide cost efficiency per square meter due to economies of scale. However, for mid-sized or smaller projects, light steel structures often emerge as the more economical choice.
3. Flexibility and Design: Creative and Functional Structures
The design flexibility of light steel structures is a major factor driving their adoption. The use of modular and prefabricated components enables architects and engineers to implement custom designs efficiently, allowing for creative architectural solutions. This adaptability is crucial for meeting the demands of modern construction, where aesthetics and functionality often go hand-in-hand.
For instance, light steel structures are frequently used in regions prone to seismic activity due to their resilience and lightweight properties. Buildings constructed with light steel are less likely to collapse during earthquakes, offering both safety and design innovation.
In contrast, reinforced concrete structures are traditionally associated with large-scale projects that require significant load-bearing capacities, such as bridges, dams, and high-rise buildings. While concrete allows for diverse designs, these often come with increased costs and extended timelines due to the laborious nature of concrete-based construction.
4. Durability and Strength: Lightweight yet Robust
Durability is a hallmark of both light steel and reinforced concrete structures, but the two materials achieve it through different mechanisms.
Light steel structures are inherently resistant to corrosion and have a long lifespan. Steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio ensures that buildings maintain structural stability under adverse conditions. Moreover, light steel components are often treated with galvanized coatings or fire-resistant materials, enhancing their resilience to both fire and moisture.
The reduced weight of light steel also minimizes stress on the building’s foundation, making it particularly advantageous for areas with poor soil conditions. For example, light steel structures are preferred in flood-prone regions where heavy foundations are impractical.
In comparison, reinforced concrete structures excel in compressive strength and fire resistance. However, they are not immune to issues such as concrete cracking or steel reinforcement corrosion, particularly in regions with high humidity or salt exposure. Over time, these issues can lead to increased maintenance costs and structural vulnerabilities.
5. Environmental Impact: Sustainable Building Solutions
In an era of heightened environmental awareness, construction practices are under scrutiny for their ecological footprints. Light steel structures emerge as a sustainable alternative due to their recyclable materials and energy-efficient insulation solutions.
Steel is one of the few materials that can be recycled indefinitely without losing its properties, reducing waste generation. Additionally, light steel structures can be equipped with green technologies, such as solar panels and thermal insulation, to improve energy efficiency and minimize carbon emissions.
On the other hand, reinforced concrete structures pose significant environmental challenges. The production of cement—a primary component of concrete—accounts for approximately 8% of global CO2 emissions. Furthermore, recycling concrete is both technically and economically challenging, often leading to its disposal as construction debris.
For projects emphasizing sustainability or seeking LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification, light steel structures represent a more environmentally responsible choice.
Real-Life Applications: Where Do They Fit Best?
To understand the practical implications of these materials, let’s explore real-world applications:
- Light Steel Structures: These are commonly used in residential housing, office complexes, modular hospitals, and temporary shelters. Their lightweight nature and adaptability make them ideal for areas with limited transportation infrastructure or urgent needs.
- Reinforced Concrete Structures: These dominate in projects requiring immense load-bearing capacities, such as stadiums, industrial facilities, and long-span bridges. They are also favored for skyscrapers in urban centers due to their compressive strength.
Conclusion
Both light steel and reinforced concrete structures play critical roles in modern construction, each catering to specific project requirements. However, the numerous benefits offered by light steel structures—such as faster assembly times, cost-efficiency, design flexibility, durability, and environmental sustainability—make them increasingly appealing for a wide range of applications.
While reinforced concrete remains a trusted choice for projects requiring heavy load-bearing capabilities or exceptional durability, light steel structures provide a dynamic, eco-friendly, and innovative alternative that aligns with the priorities of contemporary construction practices.
The decision between these materials ultimately depends on the project’s scope, budget, timeline, and environmental considerations. Nonetheless, the growing preference for light steel structures signals a shift toward more sustainable and efficient building solutions in the construction industry.
Advantages of Light Steel Structures: Click Here
See our Video List: Click Here











Leave a Reply